In Alanine, the structural isomers of α-Alanine (alpha Alanine) and β-Alanine (beta Alanine) exist.
Rational formula for α-Alanine: CH₃CH(NH₂)COOH
Rational formula for β-Alanine: NH₂C₂H₄COOH
Alanine that is widely known in the market as one of amino acids or a food additive is α-Alanine.
β-Alanine is a structural isomer of α-Alanine, which was approved to be used for healthy foods through the revision of the food and drug classification in 2019.
These 2 kinds of Alanine are said to have different tastes and roles in the body.
We manufacture and sell α-Alanine.
α-Alanine (chemical name: 2-Aminopropionic Acid) is a 3-carbon neutral amino acid with a carboxyl group and an amino group in the molecule, which is a nonessential amino acid. It has asymmetric carbon in the molecule, and there exist L-Alanine and D-Alanine in a sterically enantiomorphic relationship.
DL-Alanine, an equal mixture of L-Alanine and D-Alanine, and L-Alanine are approved to be used as food additives, and mainly used in the healthy food area.
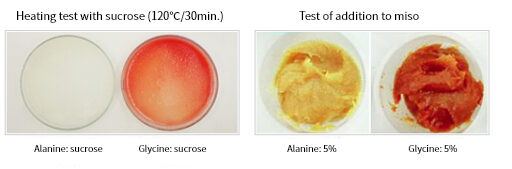
D-Alanine has been used as a synthetic raw material for agricultural chemicals and pharmaceutical products. In addition, it has been recently reported that D-Alanine has a biological activity that is different from that of L-Alanine with regard to its additive effect toward cosmetics and food.
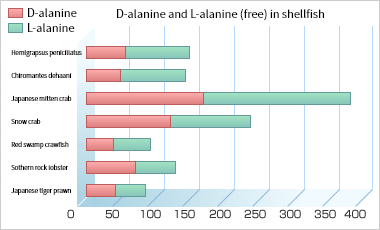
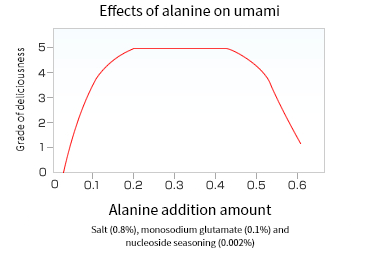
Alanine (both L-Alanine and D-Alanine) is found widely in the natural world as a proteinogenic amino acid. Further, it is known to be contained in many kinds of food, and it is said to be one of the main components of umami ingredient in delicious and popular Green soybeans.
Mulberry leaves, silk, and freshwater clams are high in Alanine as well, and it caught attention when it was reported that consuming Alanine can promote fat burning and improve liver function.
In addition to the applications to food products, Alanine’s new effect in the use for cosmetic products and the application as a plating chemical are re-evaluated.